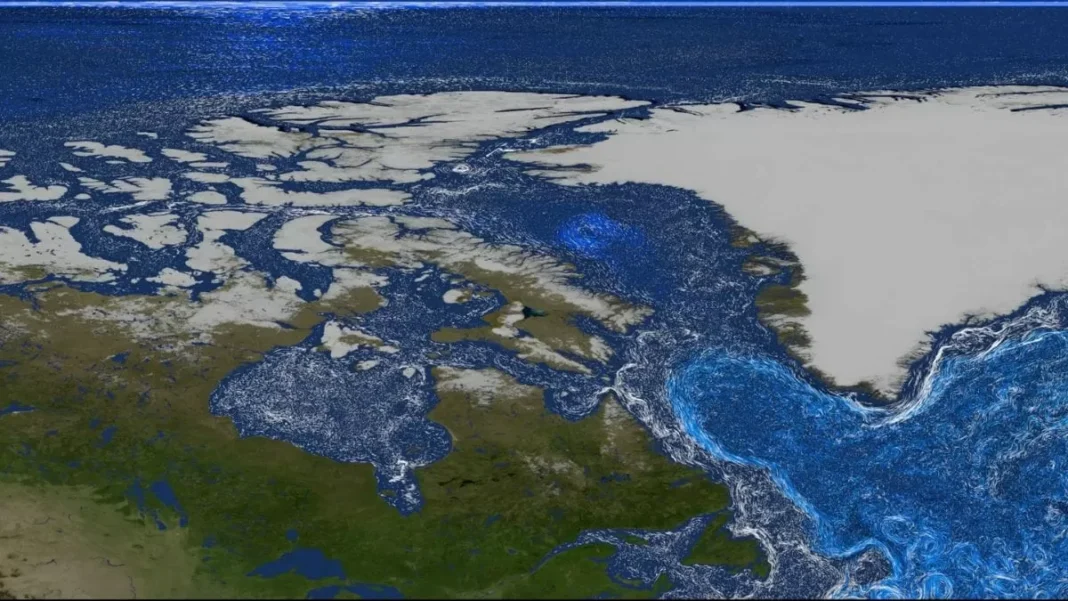
A new study by NASA has revealed some fascinating insights into the impact of Greenland’s melting glaciers on the Arctic Ocean. The findings of this study highlight the crucial role these glaciers play in fueling life in the Arctic, and their contribution to the marine ecosystem.
According to the study, each summer, massive freshwater plumes from glaciers like Jakobshavn drag deep-sea nutrients upward, boosting phytoplankton growth by up to 40%. These microscopic organisms are the foundation of the marine food web and play a crucial role in carbon absorption. The study was conducted using NASA’s ECOSTRESS (ECOsystem Spaceborne Thermal Radiometer Experiment on Space Station) instrument, which measures plant health by detecting the amount of heat radiating from the Earth’s surface.
The study’s lead author, Dr. Ian Joughin from the University of Washington, explains, “The melting glaciers in Greenland are providing a large amount of freshwater to the Arctic Ocean. This freshwater is full of nutrients that are essential for phytoplankton growth. As a result, we are seeing a significant increase in phytoplankton growth in the Arctic, which is not only beneficial for the marine ecosystem but also for the planet as a whole.”
The study’s findings are crucial as they shed light on the effects of climate change on the Arctic region. Greenland’s glaciers are melting at an alarming rate due to rising global temperatures. This causes a massive influx of freshwater into the Arctic Ocean, which has a significant impact on the marine ecosystem. The study shows that this influx of freshwater is not just a cause for concern but also has some positive aspects.
The increase in phytoplankton growth has a cascading effect on the entire marine food web. Phytoplankton are the primary producers of the ocean, and their growth provides food for small zooplankton, which, in turn, feed larger animals such as fish and whales. These larger animals are a crucial source of food for indigenous communities living in the Arctic and also play a vital role in maintaining the balance of the marine ecosystem.
Moreover, phytoplankton also play a crucial role in carbon absorption. They absorb carbon dioxide from the atmosphere through photosynthesis, which helps in reducing the amount of this greenhouse gas in the atmosphere. This is a significant finding, as the Arctic region is experiencing some of the most severe impacts of climate change, and the increase in phytoplankton growth could help mitigate some of these effects.
Dr. Joughin further adds, “The results of this study are particularly important as they highlight the connection between land and ocean. The melting glaciers in Greenland are having a positive impact on the marine ecosystem, and this is something we need to take into consideration while studying the effects of climate change on the Arctic.”
The study also has implications for future research and monitoring of the Arctic region. With the help of NASA’s ECOSTRESS instrument, scientists can continue to monitor the impact of melting glaciers on the Arctic Ocean and understand how it affects the marine ecosystem. This will provide crucial insights into the changing Arctic environment and its potential consequences for the planet.
In conclusion, the new NASA-led study has provided valuable information on the impact of Greenland’s melting glaciers on the Arctic Ocean. The findings highlight the positive effects of this phenomenon, including increased phytoplankton growth and carbon absorption. It also emphasizes the importance of considering the connection between land and ocean while studying the effects of climate change. Moving forward, it is essential to continue monitoring the Arctic region and its changing environment to better understand and mitigate the effects of climate change.